NPPGov is sharing this informative blog from Cintas. You can find the original content here.
Why Bleeding Control Kits are a Must Have for Any Business
Injuries can happen anytime and anywhere, and can result from a wide range of causes, including accidents and intentional harm. When traumatic injuries occur, saving lives is paramount. Uncontrolled bleeding is the top cause of preventable death in trauma, and approximately 20% of people who died from traumatic injuries could have survived if someone had been able to provide quick bleeding control1.
When faced with treating a traumatic injury, the first instinct may be to panic and freeze, wasting valuable time. Even if 911 is called immediately, the victim may be facing an uphill battle by the time he or she receives medical attention. The people closest to the scene of an accident can provide aid that helps to control bleeding until first responders arrive2. The greater the number of people who know how to control traumatic bleeding, the greater the chances of survival for victims3.
Organizations must be prepared for unexpected injuries and potential mass trauma situations. Organizations can help prepare by being aware of the risk, overcoming common misconceptions, training employees and providing the appropriate equipment.
RISK AWARENESS
The number one cause of preventable deaths from trauma is uncontrolled bleeding4, which accounts for 10% of all deaths in men and women5. Trauma can occur anytime and anywhere. From falling onto a sharp edge to a mass shooting, risk of uncontrolled bleeding can come in many forms, which is why awareness is just as crucial as being prepared.
With heightened awareness around uncontrolled bleeding in recent years, initiatives have emerged to help educate people about this issue. For example, the STOP THE BLEED® campaign was developed out of the need to educate the public on lifesaving techniques. The purpose of the campaign is to prepare the public to save lives if people nearby are bleeding severely6. The campaign teaches people to learn quick actions to control serious bleeding, including: call 911, apply pressure with hands, pack the wound and press and apply a tourniquet7.
The number one cause of preventable deaths from trauma is uncontrolled bleeding, which accounts for 10% of all deaths in men and women.
The Hartford Consensus is a bleeding control initiative from which the STOP THE BLEED® campaign was born. It has developed a framework for minimizing deaths as a result of school shootings, believing that preventing severe blood loss is the primary action in eliminating preventable deaths. The consensus features two major points: redefining the first responder role and training people on bleeding control, including the use of tourniquets8. According to medical professionals, a number of deaths that occurred during the 2012 Sandy Hook shooting could have been prevented had bleeding control been administered by bystanders9. Society has been greatly impacted by recent waves of casual mass shootings and subsequent deaths. Sadly, active shootings are a reality Americans must deal with, which is why understanding how to treat severe bleeding is imperative. The Hartford Consensus concludes early hemorrhage control is the key to improving survival10.
DISCLAIMER: INFORMATION PROVIDED IS FOR GENERAL PURPOSES ONLY AND DOES NOT CONSTITUTE MEDICAL, LEGAL, OR SAFETY ADVICE. LEGAL OR REGULATORY REQUIREMENTS MAY DIFFER BY LOCATION. THE INFORMATION PROVIDED HEREIN IS NOT A SUBSTITUTE FOR CONFERRING DIRECTLY WITH HEALTH, SAFETY, OR LEGAL PROFESSIONALS. CINTAS DISCLAIMS ANY AND ALL LIABILITY ASSOCIATED IN ANY WAY WITH THE INFORMATION PRESENTED, INCLUDING (BUT NOT LIMITED TO) ANY ACTION OR INACTION MADE IN RELIANCE ON THE INFORMATION PRESENTED.
UNIFORMS | FACILITY SERVICES | FIRST AID & SAFETY | FIRE PROTECTION

Common Traumatic Bleeding Misconceptions
MISCONCEPTION 1:
Traumatic bleeding won’t happen at my place of work.
An active shooter situation can occur anywhere, and gun violence is on the rise. In 2021, there were 20,726 gun deaths11. There were also 610 mass shooting events in the United States in 202012. With the frequency of mass shootings on the rise and inherent dangers in many professions, bleeding control kits should be considered for workplaces and public spaces, much like fire extinguishers and automated external defibrillators (AEDs).
Severe bleeding can also result from more common activities than people think. Falling in the workplace due to wet, split, icy steps or loose carpeting can lead to injury, such as neck, head and back injuries, as well as broken bones, sprains, cuts and pulled muscles13. Being stuck in heavy machinery is a type of accident that can happen in manufacturing, construction, farm and other industries, which in extreme cases can be deadly. These types of injuries can cause accidents that are responsible for some of the most devastating workplace injuries that can leave a worker permanently disabled or killed14.
MISCONCEPTION 2:
I don’t need a bleeding control kit if I have a first aid kit.
While a proper first aid cabinet will include a tourniquet and hemostatic agents/gauze among other lifesaving supplies, they are not purpose-built to stop severe bleeding. Bleeding control kits are designed specifically to grab off the wall and get to a severe bleeding incident as quickly as possible. The number of bleeding control kits available and where you choose to place them could be the key to saving lives15.
Consider rural powerline workers in limited resource settings. If they suffer uncontrolled bleeding and must wait for first responders to arrive, a bleeding control kit administered promptly could be the difference between life and death. But limited resource settings aren’t just in the wild. They can be in the center of a 20,000 square-foot manufacturing plant, lumber mill or warehouse — anywhere it can be challenging to reach someone experiencing a traumatic bleeding event. Each year, about 60,000 Americans die from hemorrhaging16. Depending on the type of hemorrhage, it can take only five minutes to flatline17.
MISCONCEPTION 2:
I have to be missing an appendage to use a tourniquet.
Uncontrolled bleeding can occur from various injuries, not just losing an appendage. For example, someone could be working a circular saw that kicks back and opens the radial artery on their arm. Arterial bleeding is the most severe and urgent type of bleeding, which can occur due to a penetrating injury, blunt trauma, or from damage to organs or blood vessels18. Arterial bleeding is pumped directly from the heart to the rest of the body. Consider using a tourniquet if the bleeding can’t be controlled using direct pressure, or if direct pressure can’t be effectively applied19.
MISCONCEPTION 4:
Using a tourniquet will result in losing a limb.
Many people still have the misconception that applying a tourniquet will cause the injured person to lose their limb, but this is not true. According to an article in “Verywell Heath”, tourniquets can be left on for no longer than two hours, which is why it’s important to mark the date and time of the tourniquet’s application20.
TRAINING FOR TREATING INJURY EMERGENCIES AND EXTERNAL BLEEDING
Training is critical because those closest to the scene of an accident or mass trauma situation can provide aid to control bleeding until first responders arrive. While more than 1.5 million people have been trained in emergency bleeding control, there are still millions more who can be educated21. Cintas, the largest national provider of American Heart Association (AHA) CPR and AED training, not only offers bleeding control kits but training in this area as well.
While minor bleeding is often easily controlled with a simple adhesive bandage once washed with soap and water, severe bleeding will require someone to determine if the wound is life-threatening or not.
A wound is considered life-threatening if the flow of blood is continuous and steady and if the volume of loss appears large22.
It is important to be prepared to act immediately, because certain injuries, such as cuts, regardless of size, can become more severe if, for instance, the person is on certain types of blood-thinning medications such as aspirin23.
When caring for a wound, people may confuse the terms “dressing” and “bandage.” A dressing is a clean material used directly on a wound to stop bleeding, which can be a piece of gauze or any other clean piece of cloth. A bandage, however, is material used to protect or cover an injured body part. The bandage can also be used to help keep pressure on a wound. Incidentally, a person can hold gauze dressings in place over a wound with a bandage.
When dressings and bandages fail to stop the bleeding, use of a tourniquet is required, which can be administered if the person has severe bleeding from the arm or leg24.
Implementing Bleeding Control Kits
There are two kits to consider as part of the Cintas product line: the standard kit and the premium kit.
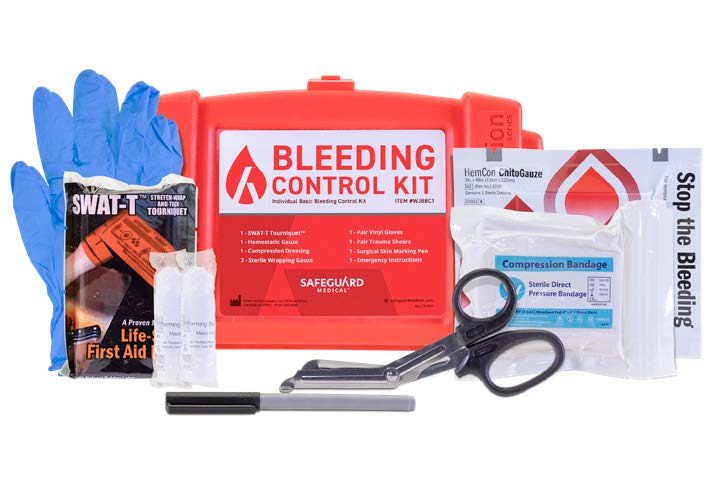
The standard kit includes a tourniquet, hemostatic gauze, compression dressing, sterile wrapping gauze, one pair of gloves, a pair of trauma sheers, a marking pen and emergency instructions.
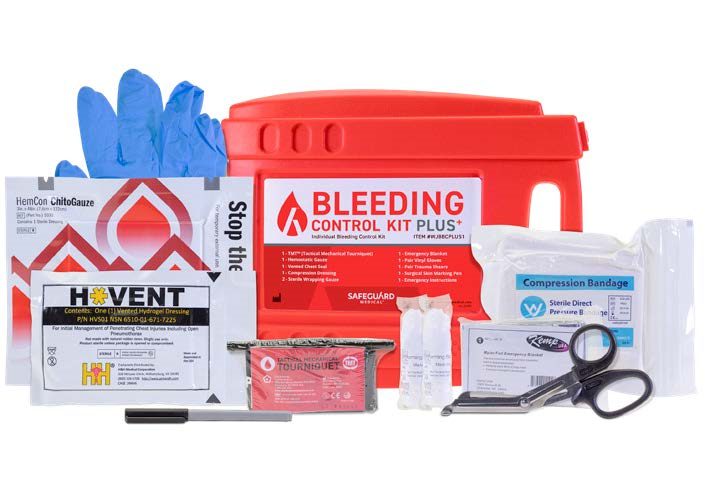
The premium kit includes all of the materials in the standard kit as well as a vented chest seal and an emergency blanket.
KIT ACCESSIBILITY
On average, emergency medical services (EMS) response time is eight minutes, whereas death from traumatic injury can happen in as little as five minutes25. Bystanders will always be first on the scene and are therefore best positioned to provide first care26.
In the workplace, at least 4 million workers suffer a nonfatal traumatic injury every year27. Organizations should consider making bleeding control kits readily available and accessible. So, how many kits should exist in the workplace? Each kit is good for one to two patients, and the number of available kits will be dependent on the unique needs of each facility. Businesses should consider making kits available based upon how frequently an area is tread. Placement of kits is ultimately up to the business and there are many considerations when deciding where to place kits.
INTERNAL COMMUNICATIONS
It’s important for employers to start a dialogue with their employees regarding the benefits and necessity of bleeding control kits as part of a comprehensive first aid program. Employers should make their workers aware of the location of bleeding control kits and offer training on how to stop severe bleeding. The more awareness of the locations of these products, along with proper training, the greater likelihood there is of applying life-saving measures.
MORE BLEEDING CONTROL KITS, MORE LIVES SAVED
There is no reason to not be prepared in case of emergency. It is with greater awareness of how and why bleeding control kits are essential tools for any environment that lives may be saved. With bleeding control kits and life-saving training, the number of preventable deaths due to hemorrhaging can decrease.
1 https://ololrmc.com/blogs/stop-the-bleed-life-saving-information-in-trauma-situations
2 https://www.uwyo.edu/wwami/stop-the-bleed/stop-the-bleed.html#:~:text=Stop%20the%20Bleed%20is%20a%20national%20campaign%20aimed,are%20generally%20the%20
first%20people%20available%20to%20assist
3 stop the bleed booklet.ashx (bleedingcontrol.org)
4 stop the bleed booklet.ashx (bleedingcontrol.org)
5 Trauma Assessment – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf (nih.gov)
6 https://www.stopthebleed.org/
7 https://www.stopthebleed.org/training
8 Creation of the first Hartford Consensus compliant elementary school in the USA | Trauma Surgery & Acute Care Open (bmj.com)
9 Hershey Medical Center Partners With ‘Stop the Bleed’ (healthymepa.com)
10 PowerPoint Presentation (azdhs.gov)
11 https://gocodes.com/heavy-equipment-accidents/
12 Gun Violence Statistics in the United States in Charts and Graphs | Reader’s Digest (rd.com)
13 Top Work-Related Injury Causes – Overview – News Directory 3
14 https://htxtriallawyers.com/blog/heavy-equipment-injuries/#:~:text=Heavy%20equipment%20can%20seriously%20injure%20workers%20and%20in,18%2C000%20other%20
injuries%20annually%20in%20the%20United%20States
15 Inadequate Placement of AED and Bleeding Control Gear Could Cost You – Campus Safety (campussafetymagazine.com)
16 https://www.360training.com/blog/basic-first-aid-skills#:~:text=A%202018%20review%20estimates%20that%20each%20year%2C%20about,can%20result%20in%20the%20
body%20eventually%20bleeding%20out
17 First Aid for Severe Trauma (FAST) Training | Red Cross
18 Types of Bleeding and How to Treat Them – First Aid Pro Perth (thefirstaidcourseperth.com.au)
19 https://sunrisehospital.com/about/newsroom/how-to-make-a-tourniquet#:~:text=Tourniquets%20should%20be%20used%20when,dealing%20with%20a%20traumatic%20wound 20 How to Use a Tourniquet Correctly (verywellhealth.com)
21 Home | Stop The Bleed
22 American Heart Association. (2021). Heartsaver: First aid, Cpr, Aed.
23 American Heart Association. (2021). Heartsaver: First aid, Cpr, Aed.
24 American Heart Association. (2021). Heartsaver: First aid, Cpr, Aed.
25 (PDF) Emergency Medical Services Response Time and Mortality in an Urban Setting (researchgate.net)
26 Stop the Bleed | Homeland Security (dhs.gov)
27 First Aid Cabinets | CPR Savers & First Aid Supply (cpr-savers.com)

